You can’t think of content creation without WordPress. While your site’s success depends on picking the right editor, Gutenberg WordPress blocks appear to be the right choice for most creators.
Since 2018, users have used either Gutenberg’s modern block system instead of the old Classic Editor.
Because it offers visual flexibility and advanced features, allowing users to get the most out from the WordPress development environment.
Today, we’ll look at both editors, comparing their strengths, the weaknesses, and how they affect your WordPress experience.
A Short History of the Gutenberg WordPress Editor
What is Gutenberg Editor?
The Gutenberg Block Editor is named after Johannes Gutenberg, who changed publishing with the movable type printing press. Inspired from this, the Gutenberg Editor in WordPress brings a modular and block-based approach to creating WordPress pages and posts.

The project was started in 2017 by WordPress co-founder Matt Mullenweg. It aims to modernize the platform and compete with Wix and Squarespace. After a lot of development, Gutenberg was launched on December 6, 2018, with WordPress 5.0.
It replaced the old Classic Editor with a flexible block system. Each piece of content is now a block that can be moved and customized. Creating complex layouts has become possible since then without needing coding skills.
Gutenberg is part of a larger plan to make WordPress a full website customization platform. It aims to make publishing accessible to everyone.
Though some users initially resisted it, it’s now WordPress’s future.
How is the New WordPress Gutenberg Editor Different from Classic Editor?
The Gutenberg Editor has introduced major changes from the Classic Editor. So many that in fact, it can be challenging to show them all at once.
A Tale of Two Editors
The WordPress Classic Editor has been the standard for years. It offers a word-processor-like experience with a single text box and a toolbar on top.
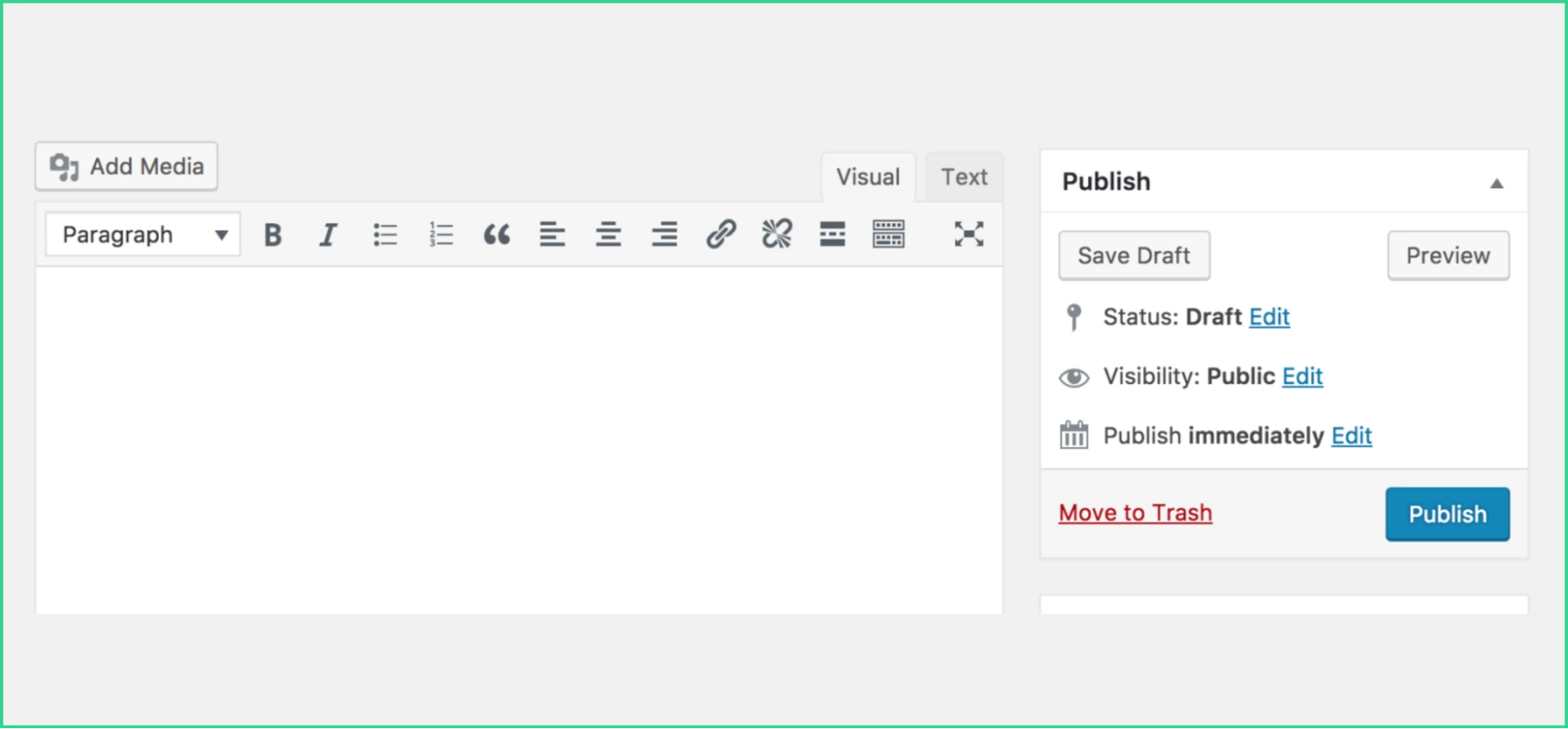
It’s similar to using Microsoft Word or Google Docs. You work on one document where all elements (text, images, and links) are together.
However, The Gutenberg Editor is different. It uses a “block-based” system. Each element of your content, such as paragraphs, headings, and images, is a separate block.
Here you can see the Heading block where a user can edit Color, Typography, Dimensions, Border, and more. Also you can transform the Heading to different blocks.
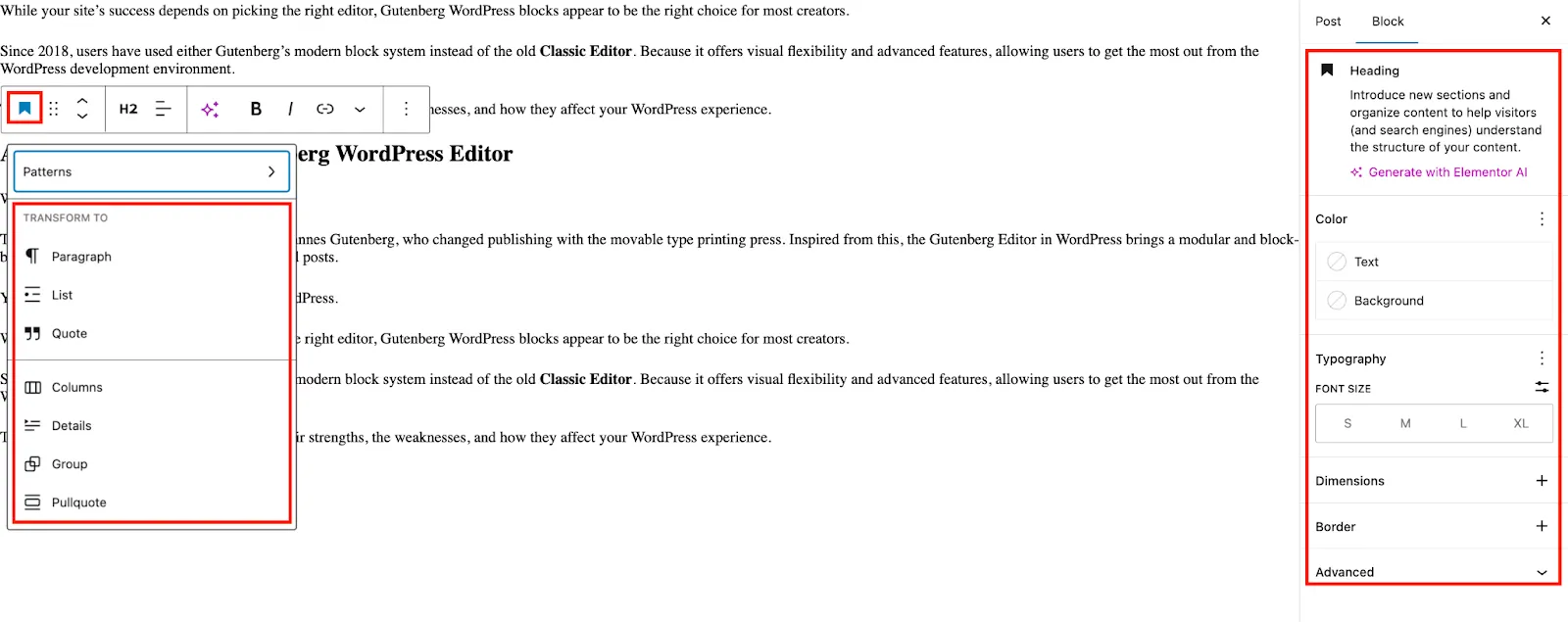
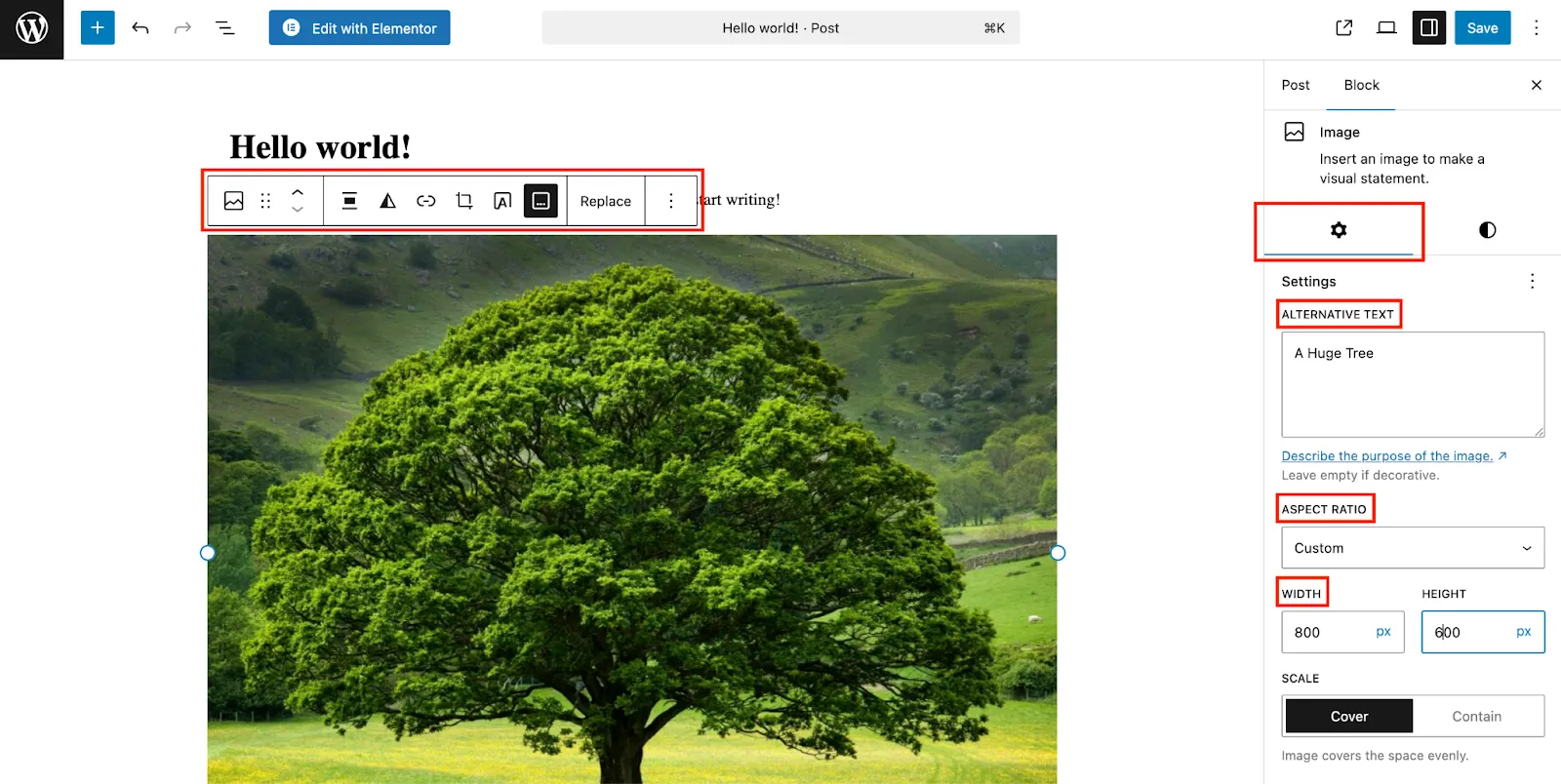
To understand the Image Block we have added an image in our post and here you can check there are two options. In Settings you can add Alt Text, Aspect Ratio with desired Width and Height.
In the Styles section, you can go after any image Filter like below. There are also useful options like Dimensions, Border, and Radius.
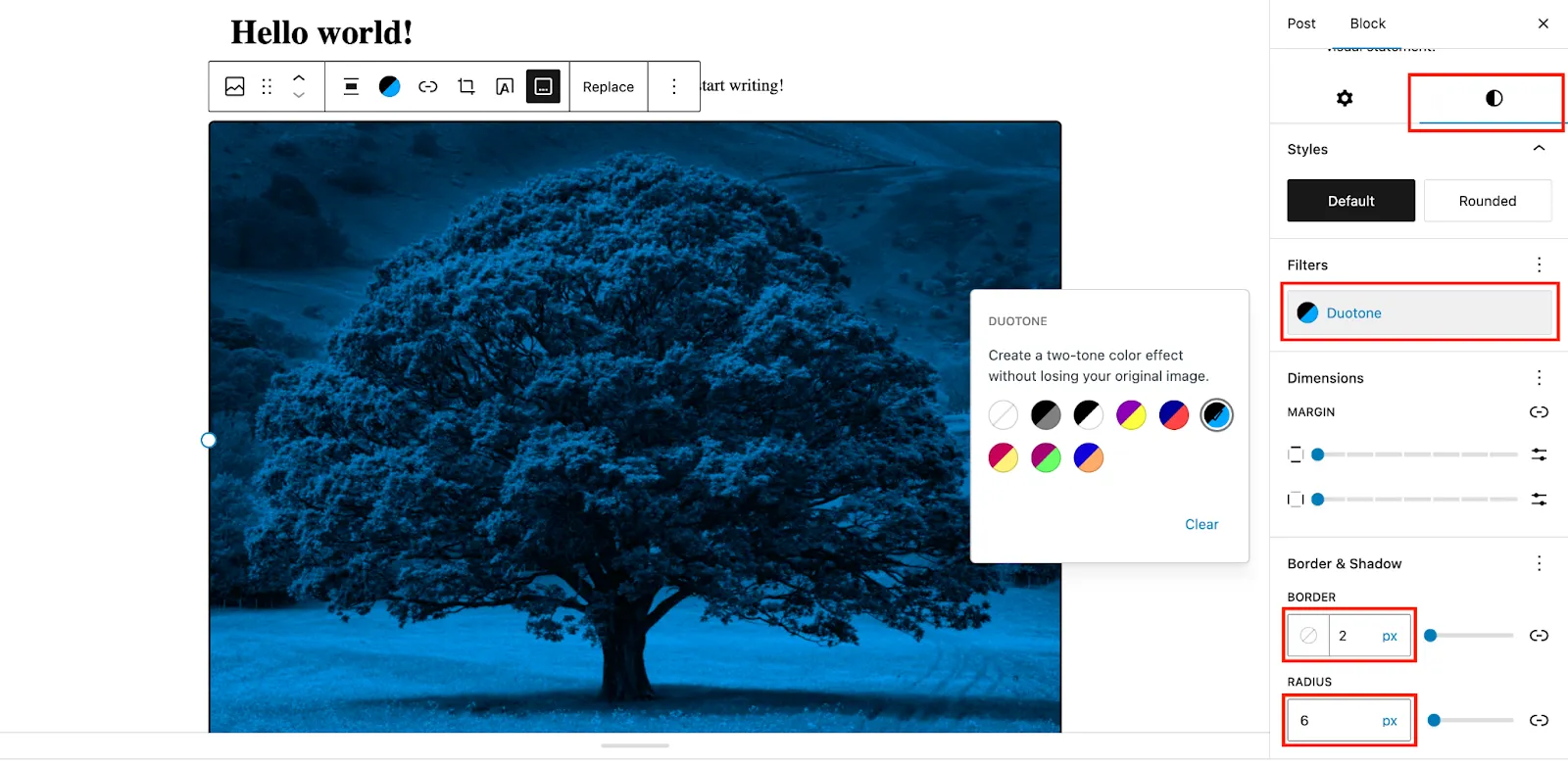
You can edit each block individually. It’s almost similar to Wix or Squarespace work.
The Block Concept: Gutenberg’s Building Blocks

To understand Gutenberg, think of your content as LEGO blocks. Each paragraph, image, heading, quote, list, or button is a block. It’ll make it easier to control each part of your content.
| Example: With the Classic Editor, adding a button requires HTML knowledge or a plugin. But with Gutenberg, you just can add a “Button” block and customize it. No coding needed |
Real-World Example: Creating a Blog Post
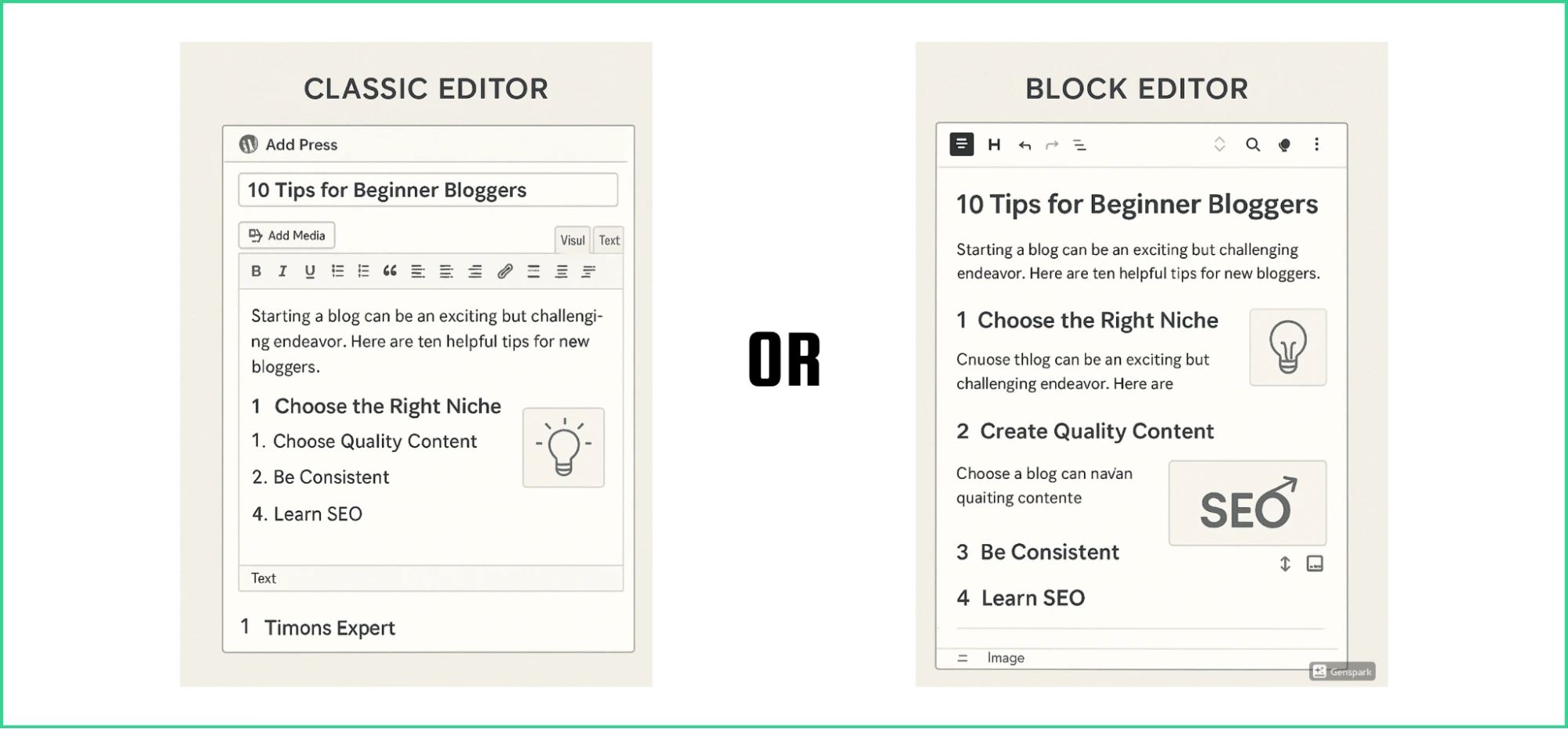
Let’s say you’re writing a blog post titled “10 Tips for Beginner Bloggers.” Here’s how the experience differs between the two editors:
Gutenberg vs Classic Editor
| Feature | Classic Editor | Gutenberg Editor | |
| 1 | Text Layout | One big text area | Title as Heading block, content in Paragraph blocks |
| 2 | Adding Images | Insert images at the cursor location | Add Image block between the content |
| 3 | Image Alignment | Can struggle with alignment | Easier control over image placement |
| 4 | Rearranging | Difficult to rearrange content | Easy drag & drop content rearrangement |
| 5 | Formatting | Single toolbar for an entire document | Each block has its own specific formatting options |
Have you got the key difference?
The Classic Editor treats your post as one whole piece. And, Gutenberg breaks it into separate content blocks. You can arrange these blocks however you need.
Major Differences Between the Two Editors
When comparing the Classic and Gutenberg editors, the main differences lie in their interface, layout options, and ease of use. Each offers unique features for different needs.
Gutenberg provides more flexibility and customization, while Classic offers simplicity for users familiar with traditional word processors.
| Category | Classic | Gutenberg | |
| 1 | Interface | A single document (like a word processor). | A set of blocks you can move and change separately. |
| 2 | Content Layout | Limited layout options unless you use custom HTML or plugins. | Offers more layout options such as columns, spacers, and media blocks. |
| 3 | Learning Curve | Easy for anyone who has used a word processor. | Requires learning the block system. |
| 4 | Customization | Limited without coding or plugins. | Lots of built-in options for colors, spacing, and layout. |
| 5 | Future Development | Still maintained, but no major updates are coming. | Actively developed with new features and blocks added regularly. |
Which Is Better? A Simple Analogy
The Classic Editor will feel like a notebook where you write everything in one flow. And, the Gutenberg Editor is more like a scrapbook. You can place text, photos, and designs wherever you want.
| Neither editor is “Bad.” They just suit different needs. If you like simplicity, Classic Editor will feel easier. If you want more control over layout and design, Gutenberg is the one you need. |
You can also use the Classic Editor as a plugin, even if Gutenberg is your default WordPress editor. Many users keep both editors and use them based on the type of content they’re creating.
How Good is Gutenberg Compared to Other Popular Alternatives?
Since its launch in 2018, Gutenberg has grown from a basic editor to a full site-building tool. It’s now moving toward Full Site Editing, which will let users design entire websites using the same intuitive block system.
Shouldn’t it be better than other popular alternatives? Let’s find out by comparing the other technical elements through this Gutenberg guide.
Gutenberg vs. Popular Alternatives
| Feature | Gutenberg | Classic | Elementor | Divi | |
| 1 | Core Functionality | Block-based editor with visual design | Simple word-processor-like interface | Drag-and-drop builder with live editing | Visual builder with inline editing |
| 2 | Cost | Free (built into WordPress core) | Free | Free version; Pro: $59–$399/year | $89/year or $249 lifetime |
| 3 | Average Page Load Time | 1.5s | 1.2s | 2.8s | 3.2s |
| 4 | Time To First Byte | 0.9s | 0.7s | 1.8s | 2.1s |
| 5 | PageSpeed Score | 93/100 | 95/100 | 81/100 | 78/100 |
| 6 | HTML Markup Efficiency | 188 lines of code | 154 lines of code | 794 lines of code | 912 lines of code |
| 7 | Pre-built Templates | Limited (patterns only) | None | 300+ (most require Pro) | 500+ layouts |
| 8 | Custom Layouts | Basic multi-column and group blocks | Limited (HTML/shortcodes) | Advanced with pixel-perfect controls | Advanced with comprehensive options |
| 9 | Animation Effects | Basic | None | Extensive | Extensive |
| 10 | Learning Curve | Moderate | Low | Moderate to High | High |
| 11 | Visual Editing | Partial (in editor) | No | Yes (true frontend editing) | Yes (inline editing) |
| 12 | Block/Widget Count | 102 core blocks | N/A | 100+ (40+ in free version) | 100+ modules |
| 13 | SEO Score | 92/100 | 94/100 | 85/100 | 78/100 |
| 14 | Core Web Vitals | High | Highest | Medium | Low |
| 15 | WooCommerce Integration | 26+ dedicated blocks | Basic | 20+ widgets (Pro only) | Extensive |
| 16 | Theme Builder | Basic (FSE in progress) | No | Yes (Pro only) | Yes |
| 17 | Dynamic Content | Yes (with core blocks) | No | Yes (Pro only) | Yes |
| 18 | Code Output | Clean | Cleanest | Heavier | Heaviest |
| 19 | Custom CSS Access | Yes | Limited | Extensive | Extensive |
| 20 | Third-party Compatibility | Excellent | Good | Very Good | Good |
Everything You Need to Know About the New WordPress Editor
The Gutenberg WordPress uses blocks that can be combined to make rich content without coding. It’s not just for editing pages and posts. Getting started with Gutenberg gives you the freedom to customize the whole site, including headers, footers, templates, and layouts.
Anyone working with modern WordPress websites should understand the Block Editor’s interface, settings, buttons, and block system.
Interface
The Block Editor is designed for ease of use, with a simple layout that makes content creation easy and powerful.
It has several parts that work together, making editing smooth.
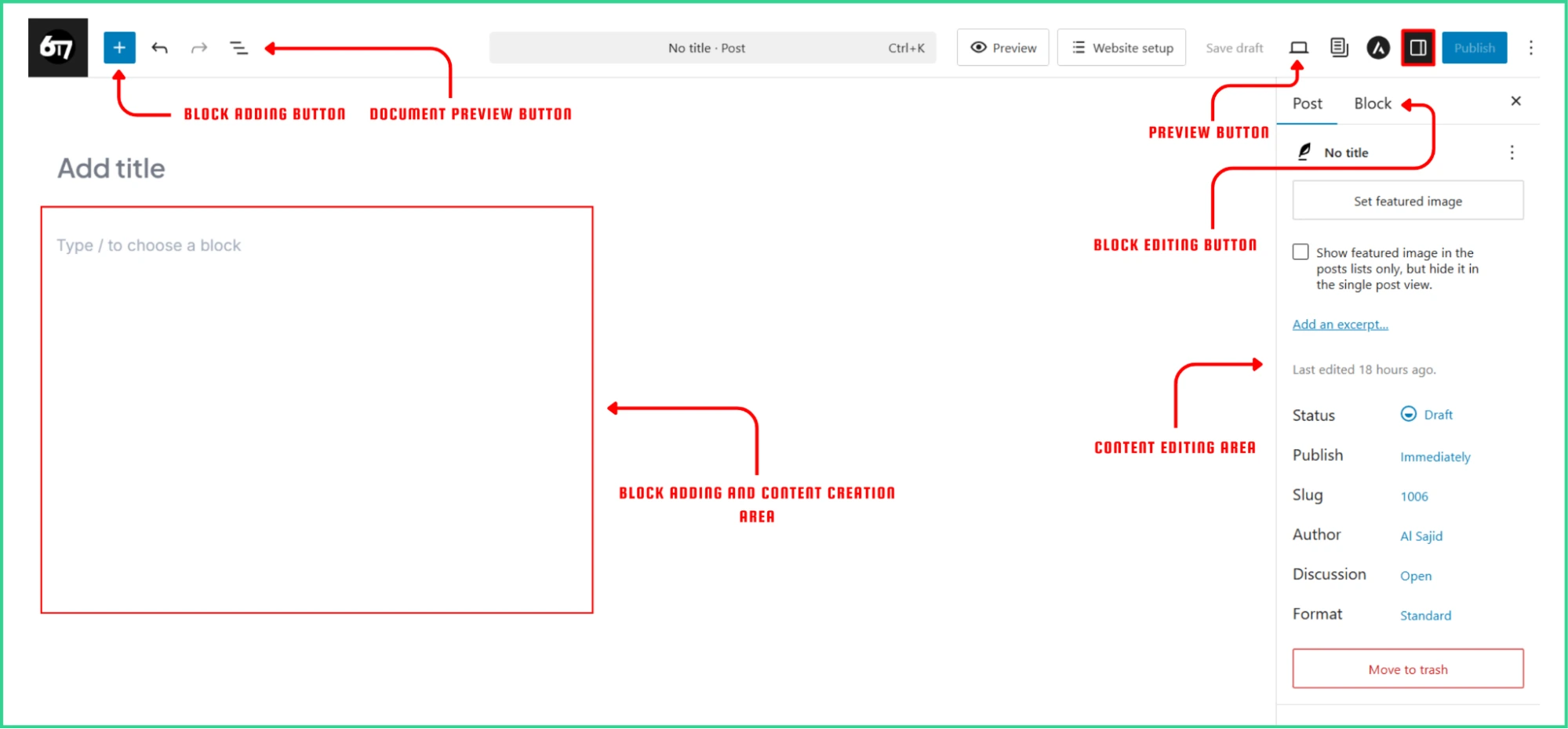
In the Block Adding Area, you can add and edit blocks.. This space shows exactly how the content will format, offering a What-You-See-Is-What-You-Get experience.
The Block Inserter is the main tool for adding content. It’s located in the top-left corner and can be opened with the blue “+” button.
In the panel, you will see all available blocks by category and name.
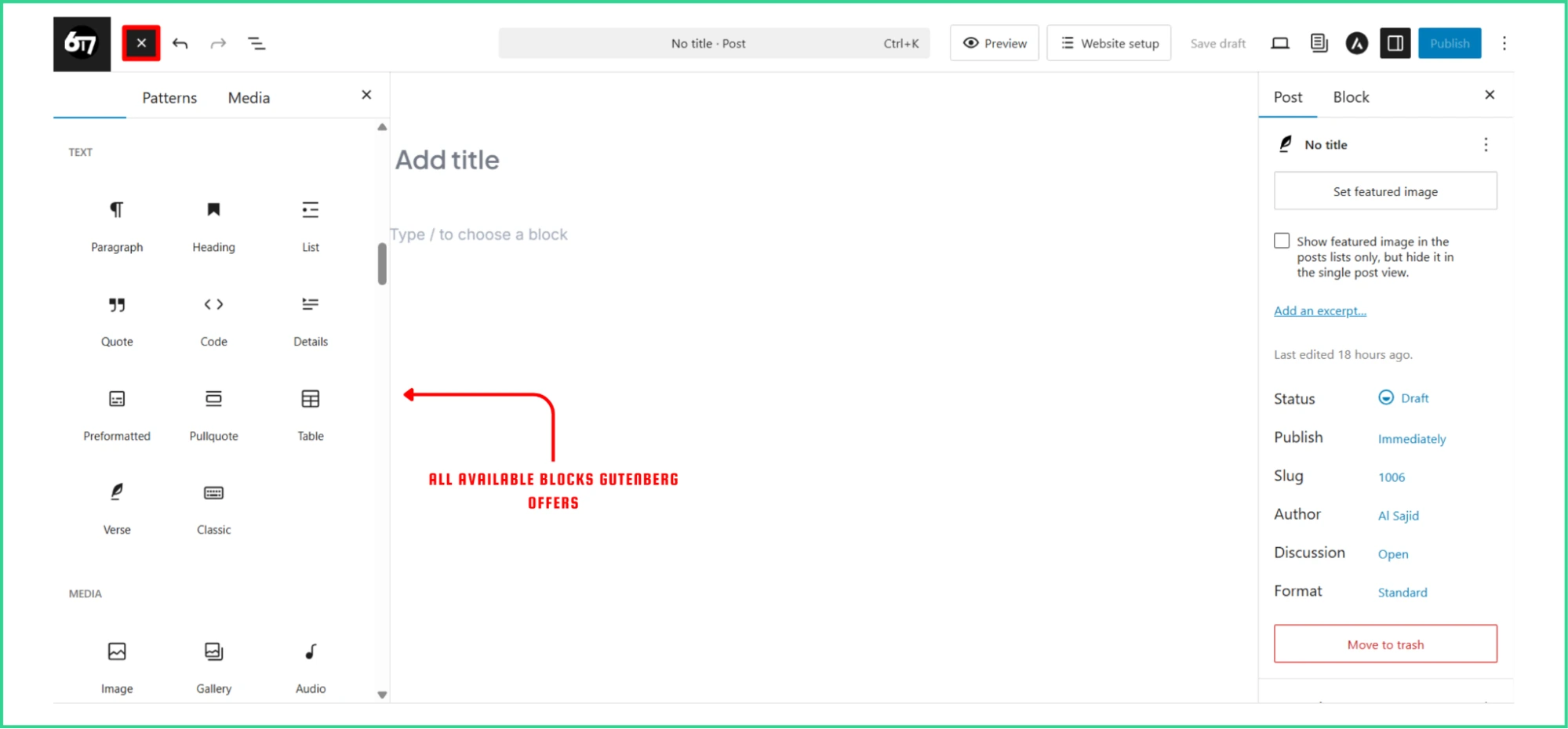
Users can browse or search for text, media, design, and widget blocks.
There’s also a Patterns tab that offers pre-designed block combinations (If you have any) for quick page sections.
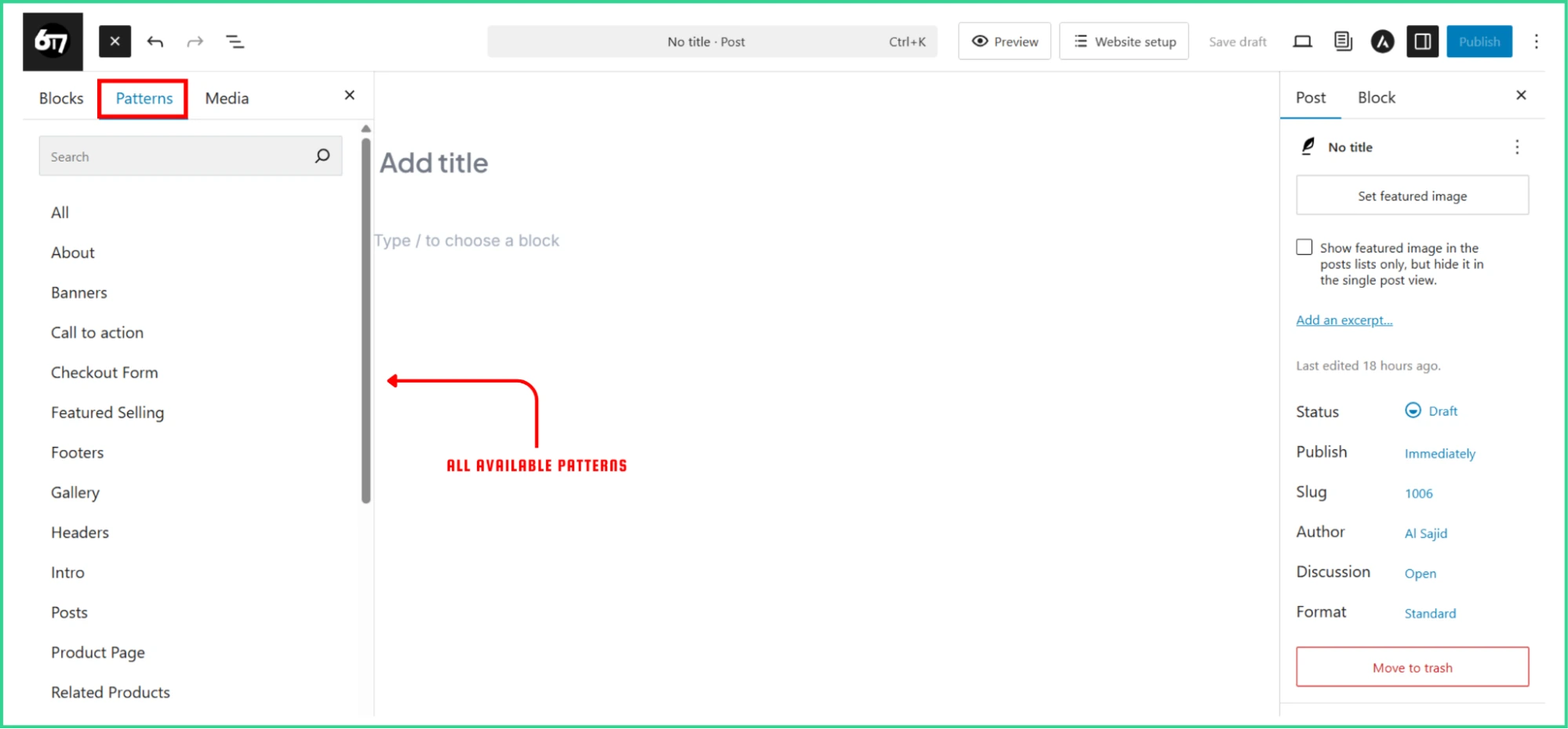
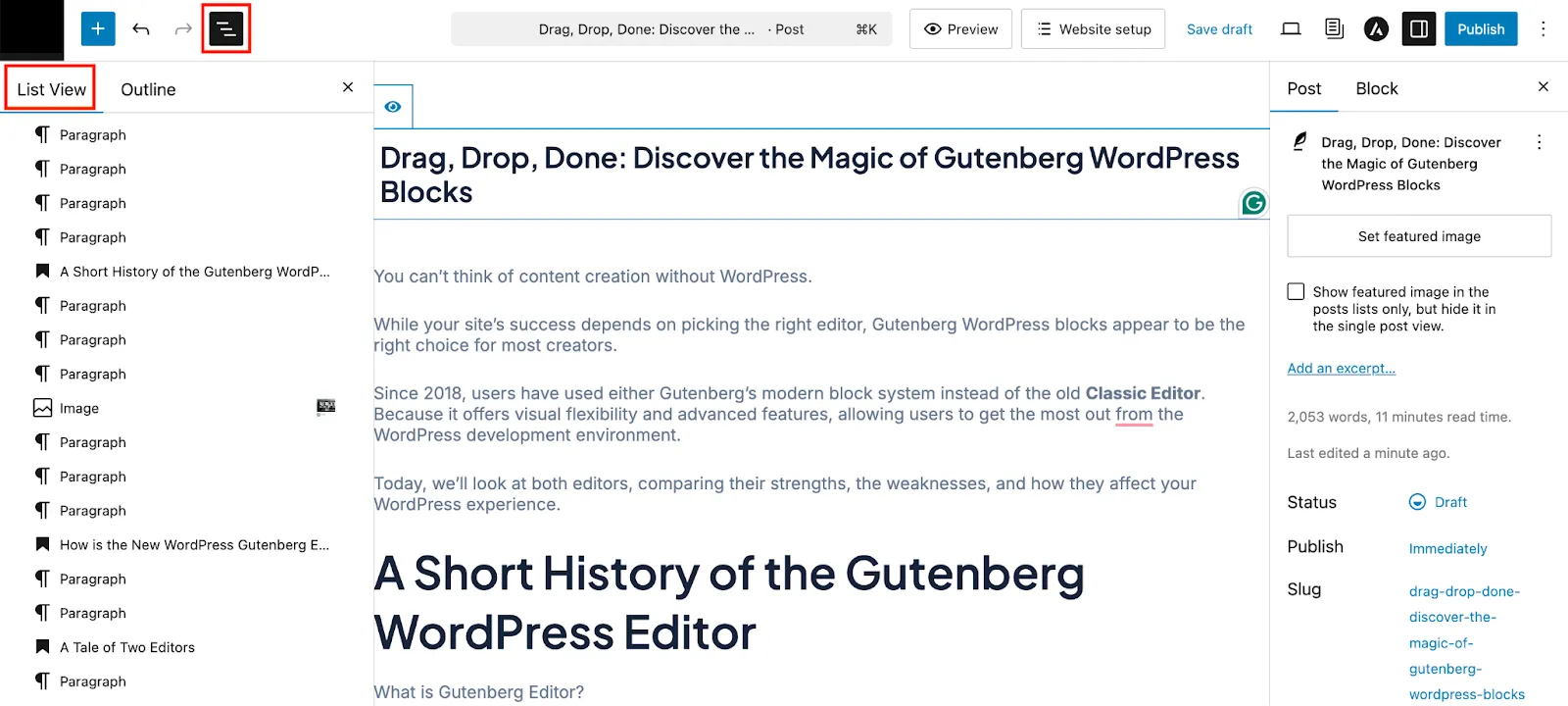
One of the best features of Gutenberg is the Document Preview secretion that lets you see all the added blocks in a list format. There are two options, one is List View- here, you can see all the paragraphs, headings, and images of a post.
This helps manage content more effortlessly, giving a clear overview of all blocks on the page.
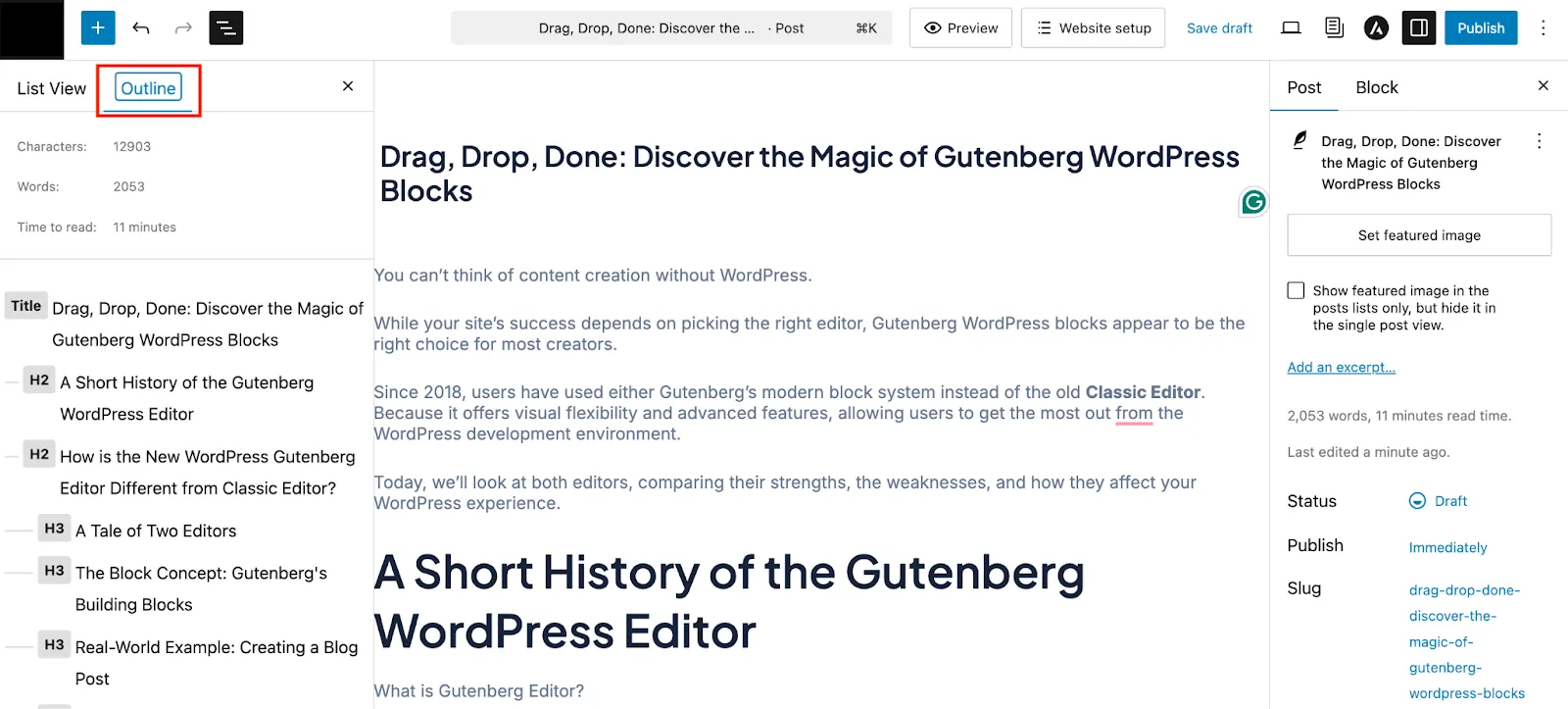
Second one is Outline. In this section you can check the total Characters, Words, and Time to Read this post.
| You can Grab, Move, and Drop blocks in the Document Preview as well. |
Another useful feature is the Undo/Redo button, that lets you undo the most recent action.
Quick shortcut for a simple mistake!
Settings
The Block Editor’s Settings system has two levels: Document Settings and Block Settings.
Both are accessible through the Settings panel on the right side, which appears when you click the Button.
Clicking on the Block will give you access to some additional settings for added blocks.
Well, the Block Setting is different for every type of Block available or installed on your WordPress site.
The Post Settings control the main properties of the page or post. This includes the title, permalink, featured image, excerpt, and discussion settings. You can also find advanced options like custom fields, page attributes (for hierarchical content), and scheduling options.
However, Block Settings let you control individual block and their appearance. When you select a block, it switches between options specific to that block, like –
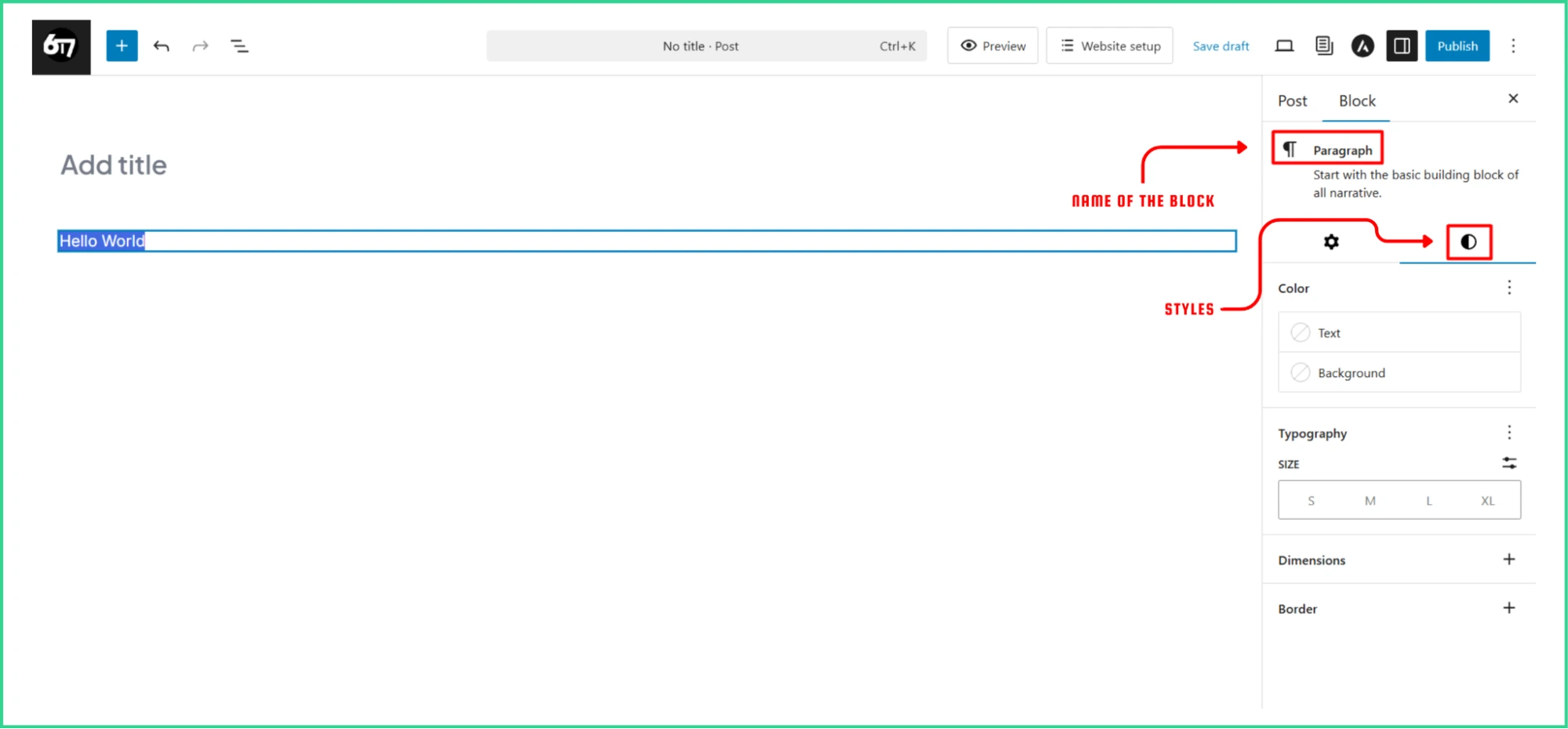
| Category | Details | |
| 1 | Styling Options | Colors, typography, spacing, and alignment |
| 2 | Content Settings | Link destinations, image alt text, and media options |
| 3 | Layout Controls | Margins, padding, and responsiveness |
| 4 | Advanced Settings | CSS classes, HTML anchors, and custom attributes |
Lastly, block locking options are available to prevent accidental changes or deletions of important content.
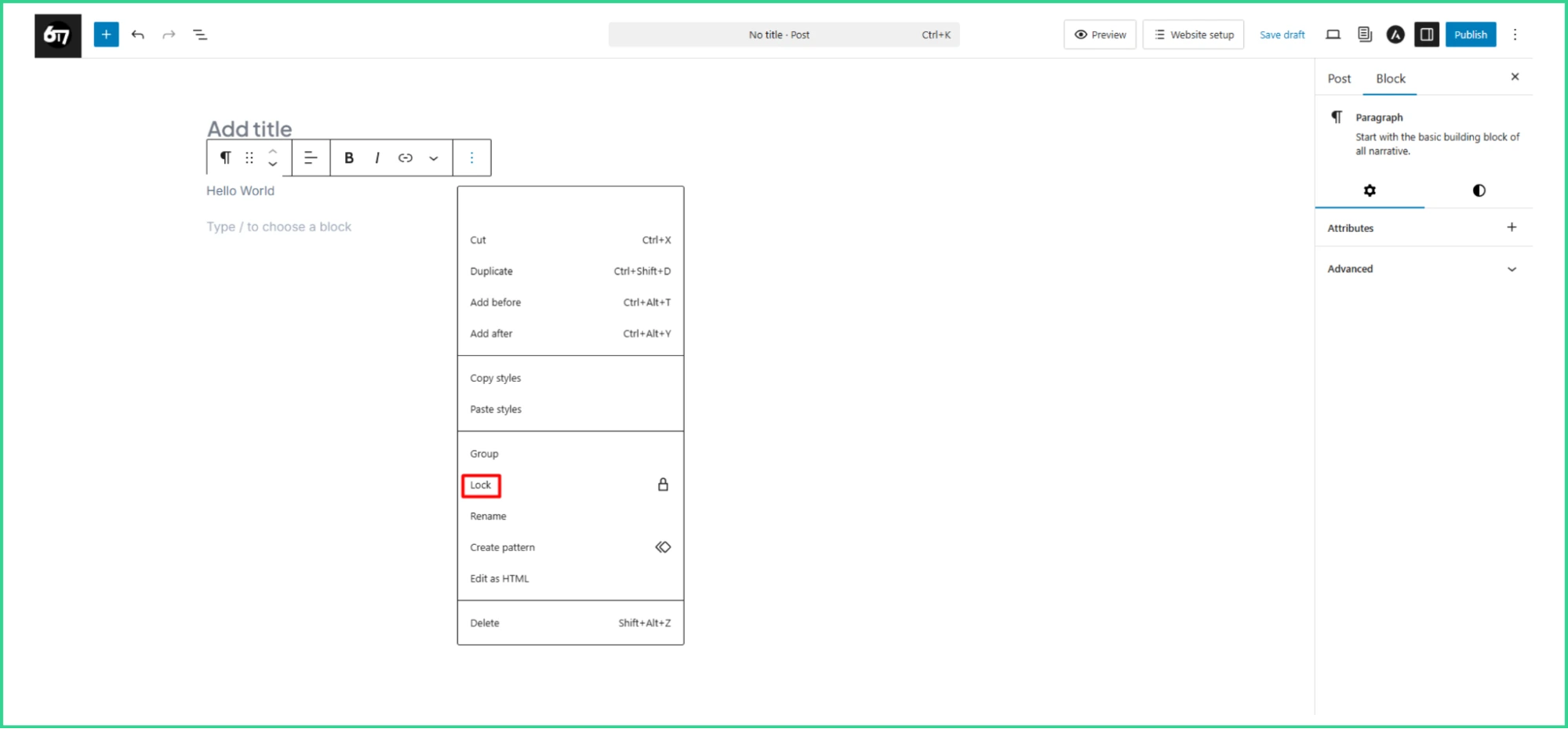
This is especially useful for sites with multiple editors or when you need to protect key layout elements.
Buttons
The Button system in the Block Editor includes both interface navigation buttons and the Buttons block used to create elements in content.
Interface buttons are key to the editor’s navigation and functionality. The main Block Inserter button (blue “+”) opens all available blocks and patterns.
In the editing area, contextual buttons appear depending on the selected content.
Block-specific toolbars show above selected blocks with formatting and configuration options.
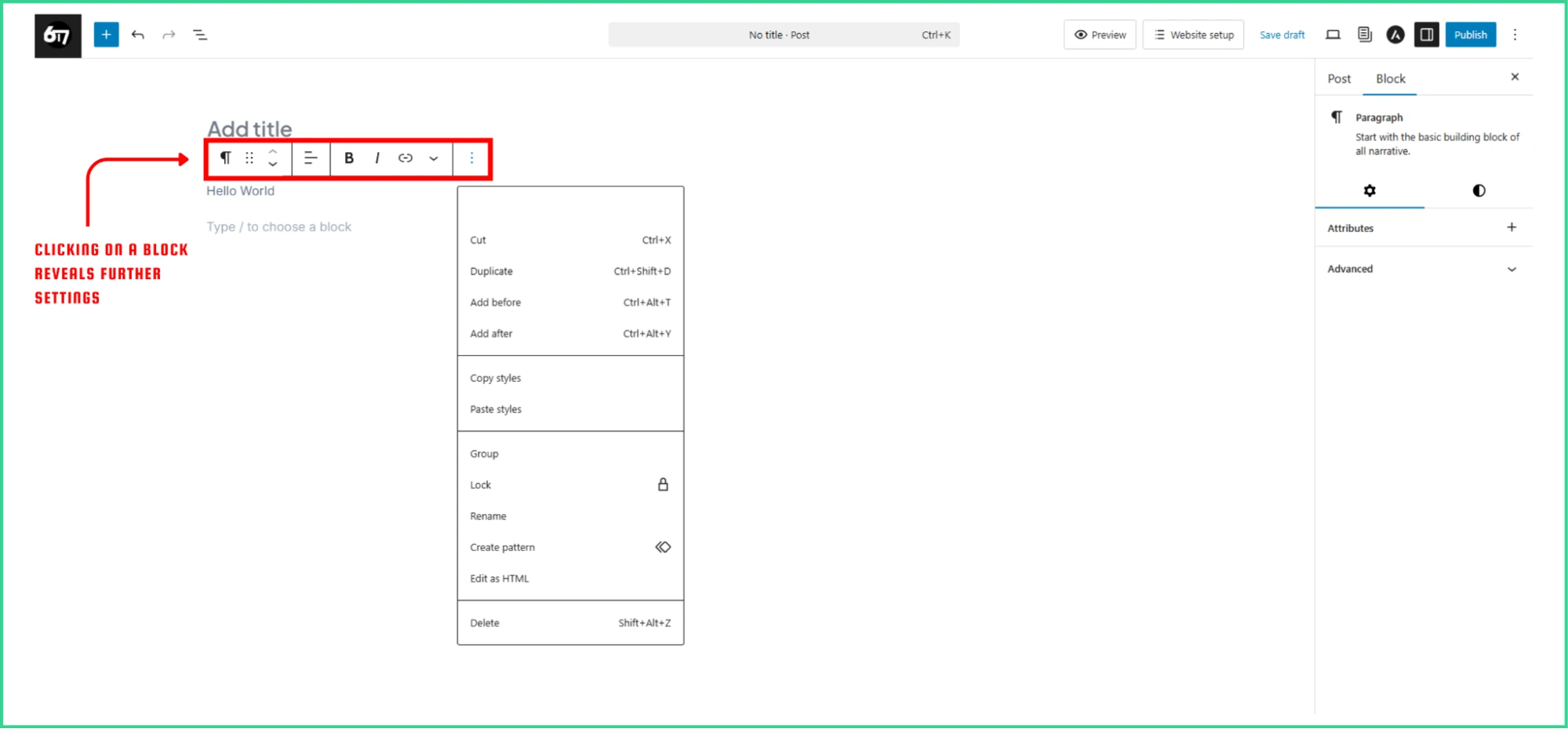
Text blocks offer controls for bold, italic, links, and alignment. Image blocks allow for replacement, cropping, and caption editing.
The Block Toolbar is an important part of the button system. It appears above selected blocks and usually includes:
- A block-type selector to change the block type.
- A drag handle to move blocks.
- Up/down arrows to adjust block placement.
- Alignment controls for the block.
- Formatting options for the content.
- A more options menu (three dots) for extra actions like duplication, grouping, and block conversion.
Every button on Gutenberg is a powerful tool for adding styles and adding additional customization options.
Blocks
Blocks are the basic units in the Gutenberg. They change how you create content, moving from a simple text format to a more modular and multimedia approach.
Each block has a specific purpose and offers its own settings and styling options. They belong in specific Types, including:
Text Blocks

Text blocks are the core for writing content. They include Paragraph blocks for text, Heading blocks for structure and SEO, and List blocks for bullet or numbered lists.
Media Blocks

Media blocks help you add multimedia. The Image block lets you add responsive images with captions, alt text, and links. Gallery blocks create image collections with different layouts.
Design Blocks

Design blocks help with layout and structure. The Columns block creates responsive columns. Group and Stack blocks help organize content. Spacer blocks add white space, and Separator blocks divide sections of content visually.
Widget Blocks

Widget blocks bring the classic WordPress widgets into the block system. These include blocks like Recent Posts, Categories, Tag Cloud, Search, and Social Icons.
Add More Blocks
The flexibility of the Gutenberg WordPress editor allows you to use additional advanced blocks plugins created by third-party developers. These additional Gutenberg blocks enhance the functionality of Gutenberg and offer you more options to create visually appealing websites.
For instance, you can use the WPMozo Blocks and Addons plugin that offers more than 10 free Gutenberg blocks.
This single plugin adds various blocks to meet different design requirements, enabling you to make the most of your Gutenberg editor. You can design headings with multiple colors or font types; add an image flip box with content and a button. Furthermore, expect more blocks in the library when the plugin gets updates.
Thus, you are fully benefited when you choose the Gutenberg editor as your primary WordPress page builder.
WordPress Classic Editor vs Gutenberg: Why it is 10 Times Better and Performs Well
After reviewing its performance and usage, it’s clear that the WordPress Classic Editor still offers many benefits. But those requiring additional tasks will definitely admire Gutenberg of WordPress.
Gutenberg keeps on adding new features. Its easy-to-use interface is perfect for those who want an efficient editing experience.
The Classic Editor is still a powerful tool that works well for millions of users. While Gutenberg offers more design flexibility, the Classic Editor lacks in speed, reliability, and ease of use.




0 Comments