WooCommerce allows flexibility to all kinds of websites. User roles and their permissions are one example of this. A website can have roles for Authors, Editors, and the obvious Site Admin.
The capabilities of these user roles vary. The site admin is the only one who can create new or delete existing roles. A majority of the websites powered with WordPress are managed by teams, as found in this 2023 survey.
Having the know-how of WooCommerce User Roles and their capabilities is important for all website owners. They can effectively manage their sites, and assign appropriate permissions to different team members.
Here, we will provide a complete guide about the different user roles and how to manage their permissions.
Understanding WordPress User Roles
WordPress comes with six defined user roles. The administrator role is automatically assigned to the website’s creator. It has all the permissions enabled and control over every setting.
Then come the other roles, which the administrator can create and assign to other users. These user roles have varying capabilities. For example, the Editor role is designed to edit, update, and delete posts added by other users.
Access the following tab in the dashboard menu to view or edit WordPress user roles.
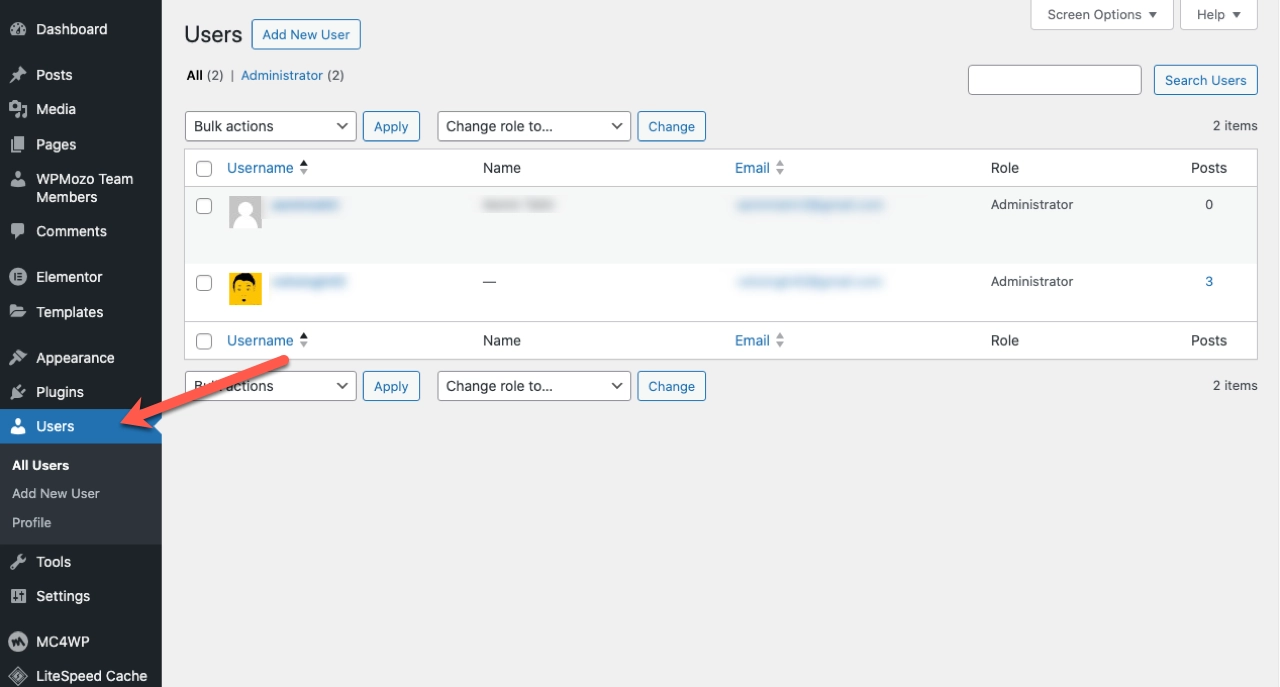
Here is an overview of the 6 WordPress user roles and what they can do:
- Administrator: The site Administrator controls all the settings. They can manage existing users or add new ones. In short, the do-all role is that of the administrator on WordPress.
- Author: An Author can add new content or posts to a website. They can also edit or delete their old posts. However, an author cannot edit or delete content added by other users.
- Editor: The role of the Editor grants a user additional permission. They can manage, edit, or delete posts published by all other users on the website.
- Contributor: A user with a Contributor role can edit certain posts and even delete them. However, they can’t make changes to posts that are excluded from their capabilities.
- Subscriber: A subscriber can only read the posts of a website. No edit or other permissions are granted to subscribers.
WooCommerce User Roles and Capabilities: An Overview
After looking at WordPress roles, we will now explore the additional user roles that WooCommerce has to offer.
WooCommerce adds more features to the already feature-rich platform that WordPress is. As WordPress’ default features focus more on the blogging side, installing the WooCommerce plugin means you have access to e-commerce-related functions.
The same applies to users. WordPress user roles allow you to manage content permissions. The WooCommerce user roles have slightly different capabilities.
For example, a customer role is given to everyone who makes purchases in your online store. The customer cannot make any changes to the store or its contents. They can only manage their own cart and their personal information and add or remove payment methods.
Then there is the role of the Shop Manager. It has more permissions and is capable of changing the articles on a store.
Let’s look at the different WooCommerce roles in detail:
1. Customer
The customer role is assigned automatically to all buyers of an online store. Sometimes, they can make purchases as guests, which doesn’t require a customer account.
However, once a customer creates an account, they are given a set of capabilities & permissions. These mostly relate to their personal choices and information.
Here’s the login page of a customer account on a typical WooCommerce store.
Once a customer creates or logs in to an existing account, they will see more options. For example, look at the following screenshot of the settings of a customer account.
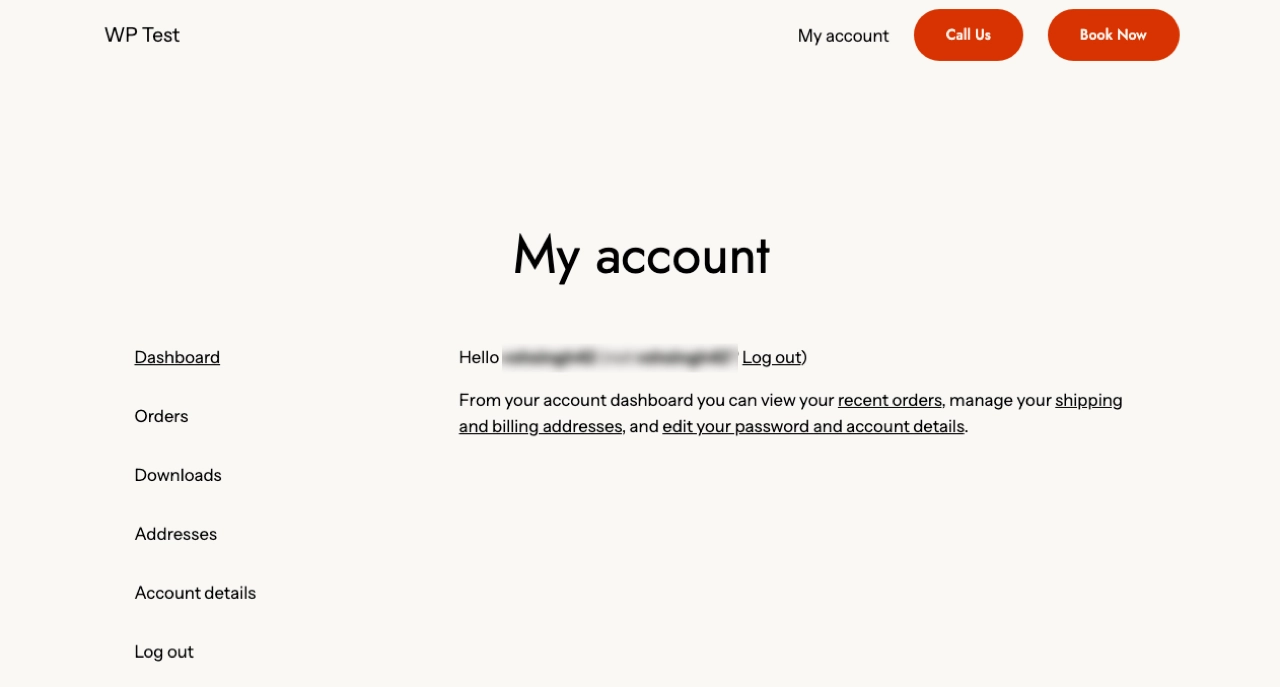
As you can see, the customer can manage a range of settings and information. They can check their previous orders and see the status of pending ones.
Similarly, a customer can manage personal information such as addresses and billing details. Overall, the customer mostly deals with settings related to their own purchases and details.
2. Shop Manager
The shop manager can edit and update items in the store. This also includes access to detailed store statistics, reports, and other information. WooCommerce provides the shop manager with all the control over the store.
The following screenshot displays the menu tabs you can access from your dashboard as a shop manager.
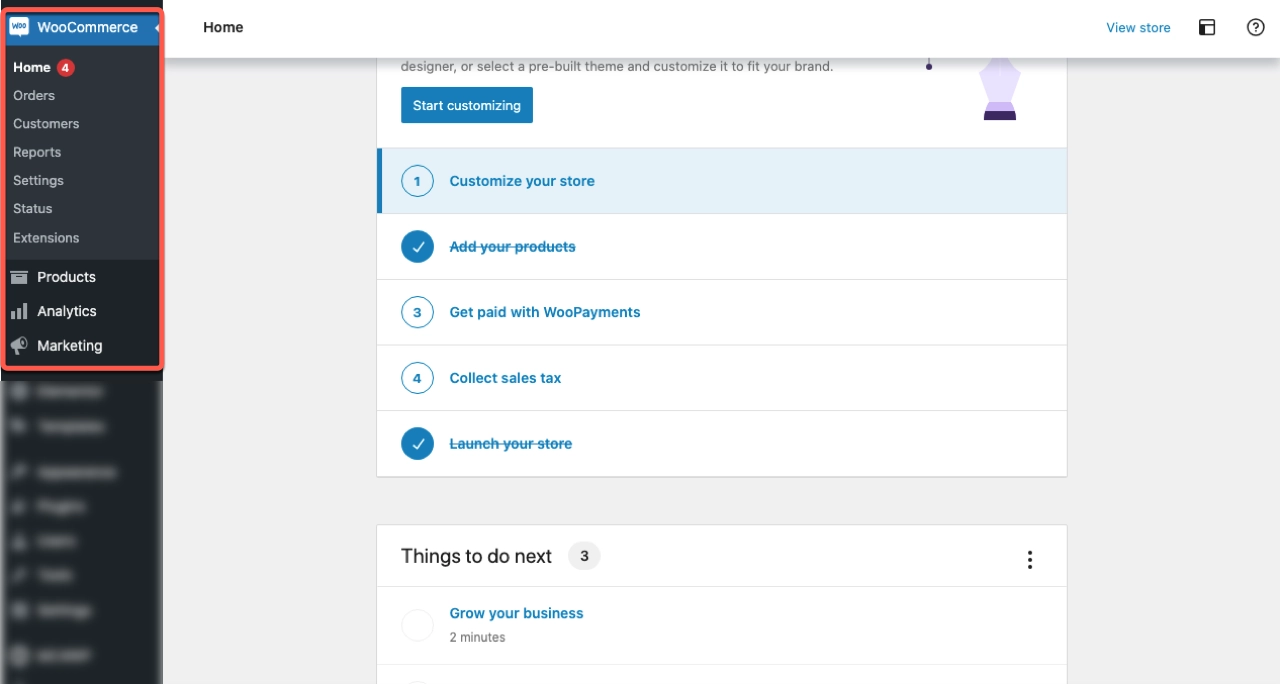
As you can see, the shop manager can view and manage orders, manage customers, see reports & order status, and update settings. Apart from this, the shop managers can change the appearance of their store as well.
The role of shop manager has vast capabilities. Additionally, they can manage the permissions or account settings of customers as well. Depending on if they are the WordPress administrator, shop owners can create new custom roles too.
A shop manager is typically responsible for adding new items to the website. They have to analyze the stats and then act accordingly. They are also responsible for the pricing of items and billing settings.
Managing User Roles & Capabilities
A site administrator can manage all the roles assigned on their website. Similarly, they can assign roles to new users with their desired capabilities. WooCommerce roles vary slightly.
A WooCommerce shop manager can edit customer capabilities, and create custom roles. However, those are restricted in their capabilities too.
Here, we will walk you through the process of managing user roles & capabilities both on WordPress and then WooCommerce.
Managing WordPress User Roles
As we have learned, WordPress has six types of user roles. By default, the site owner has the Administrator role. That user can then add new users with specific roles.
To add a new user, first, the site administrator will go to the Users menu from the dashboard. A list of all the current users will be available there.
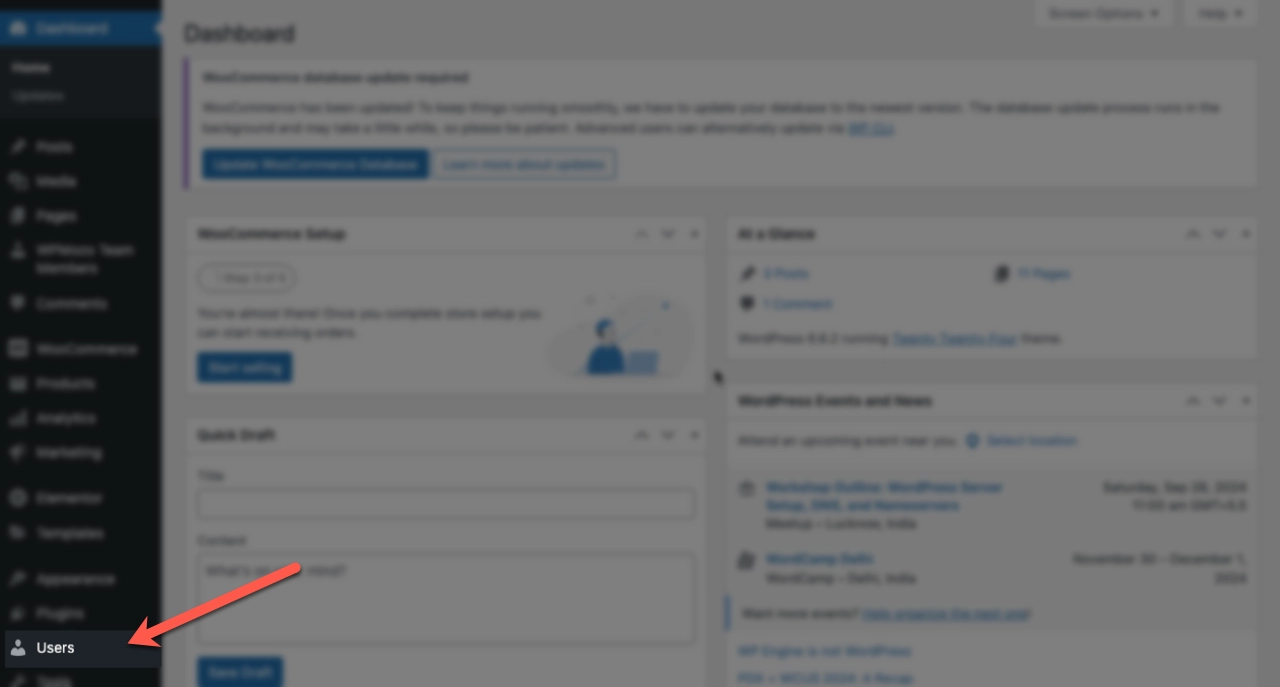
After clicking on Add New User, they will have to provide the details asked. This includes the username, an email, and a custom password for that user.
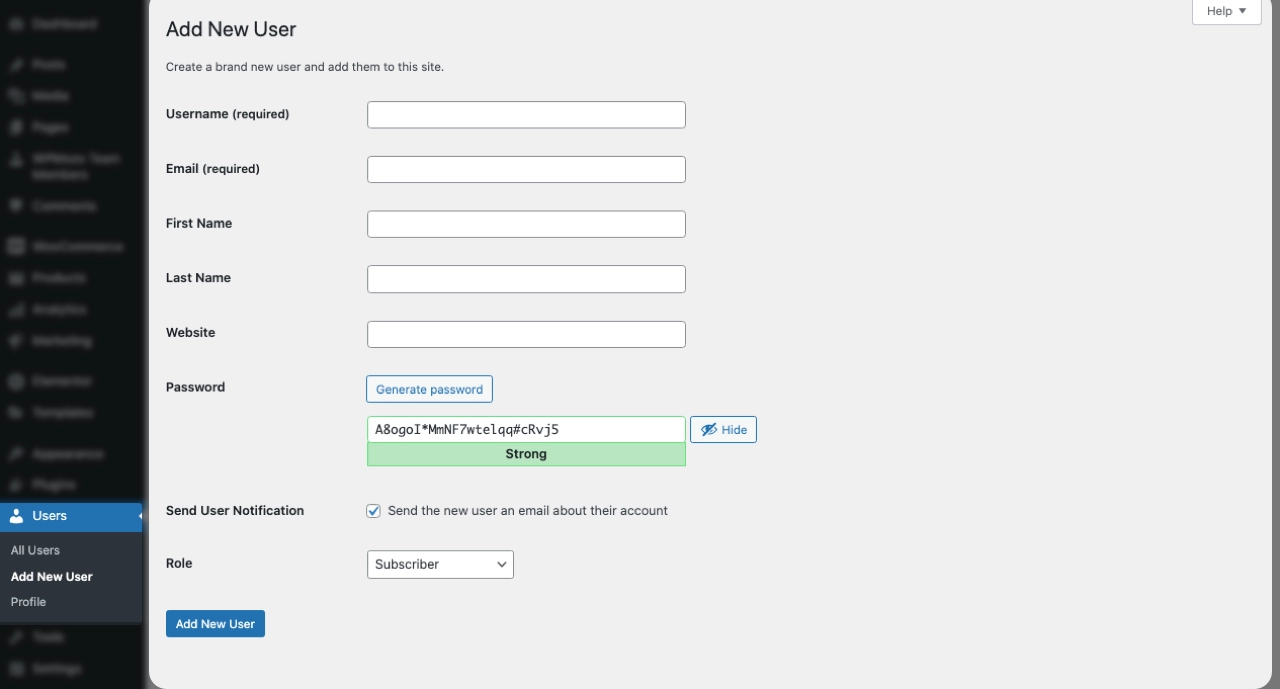
After entering this information, they can select the type of user role based on the desired permissions. Once done, clicking on the “Add New User” button at the bottom will complete the action.
Old user roles can be deleted from the same page.
Managing WooCommerce User Roles
The WordPress administrator is automatically the store’s shop manager. They can further customize the settings according to their requirements.
To manage the customer role, you should click on the “Customers” tab from the WooCommerce dashboard menu. The following screenshot shows the customer management interface and overview tab.
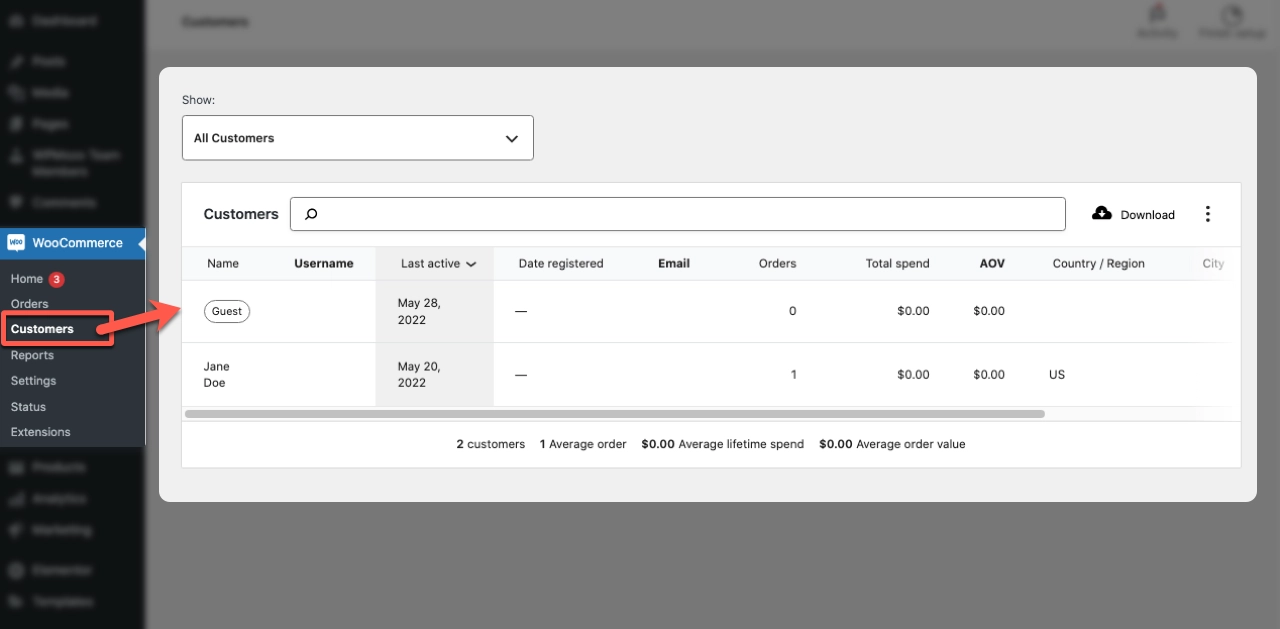
Here, all customer data is displayed and can be managed accordingly.
Apart from this, WooCommerce shop managers can manage account creation from the WooCommerce settings. Here’s a screenshot of where you can find this tab.
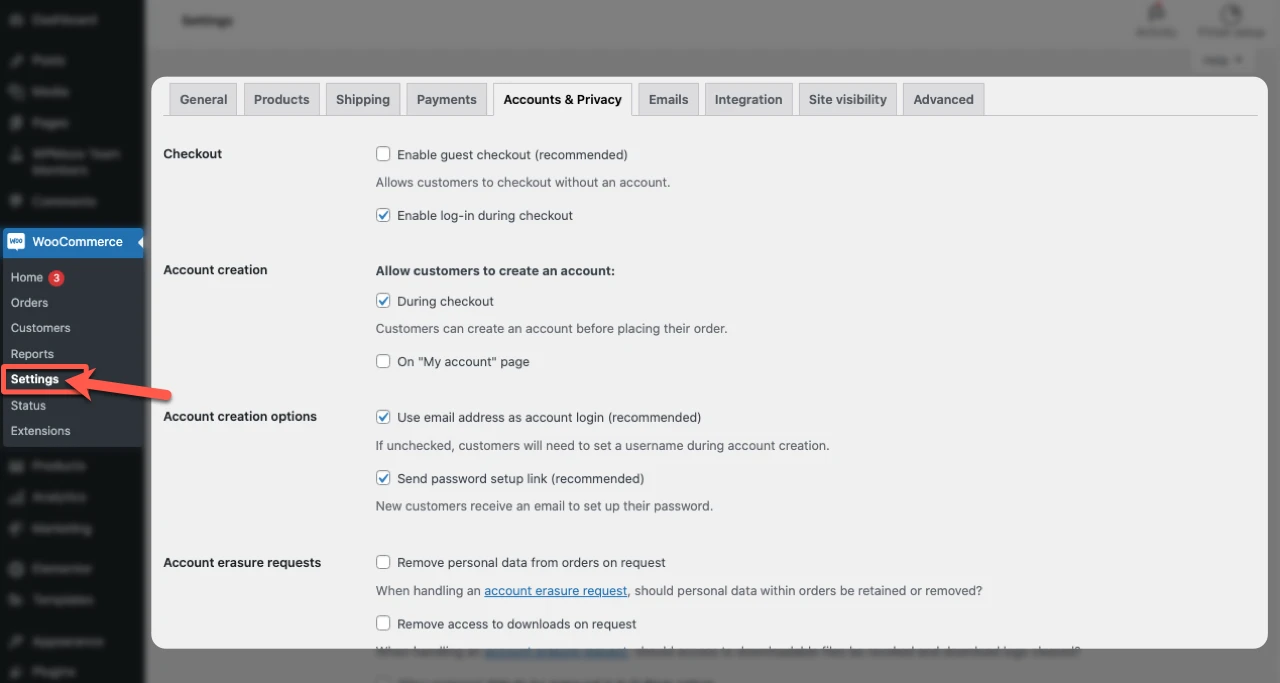
You can enable or disable account creation, and also choose if you want to make it mandatory for customers. The capabilities and other information can be managed from the same Settings.
Security Considerations
Website administrators need to consider the security implications of user roles. For example, the website owner should only assign roles with limited capabilities to new users.
Once the user is ready, new roles can be assigned with advanced permissions. Similarly, it is important to regularly audit the website.
For WooCommerce, the shop manager should check all of the customer account settings before enabling anything new. Similarly, all user capabilities must be double-checked before creating custom roles on WooCommerce.
Wrapping Up
WordPress’ multi-user feature allows website owners to work with a team on their website. The same goes for WooCommerce, which has some advanced user roles and capabilities.
Once a WooCommerce shop is created, the shop manager can adjust the settings to allow customers to create an account. Within this, they can customize their permissions and capabilities.
Apart from this, the Settings menu on WooCommerce allows managers to create custom roles for their stores. Additionally, they can change the settings to require new customers to make an account on their first purchase.





0 Comments